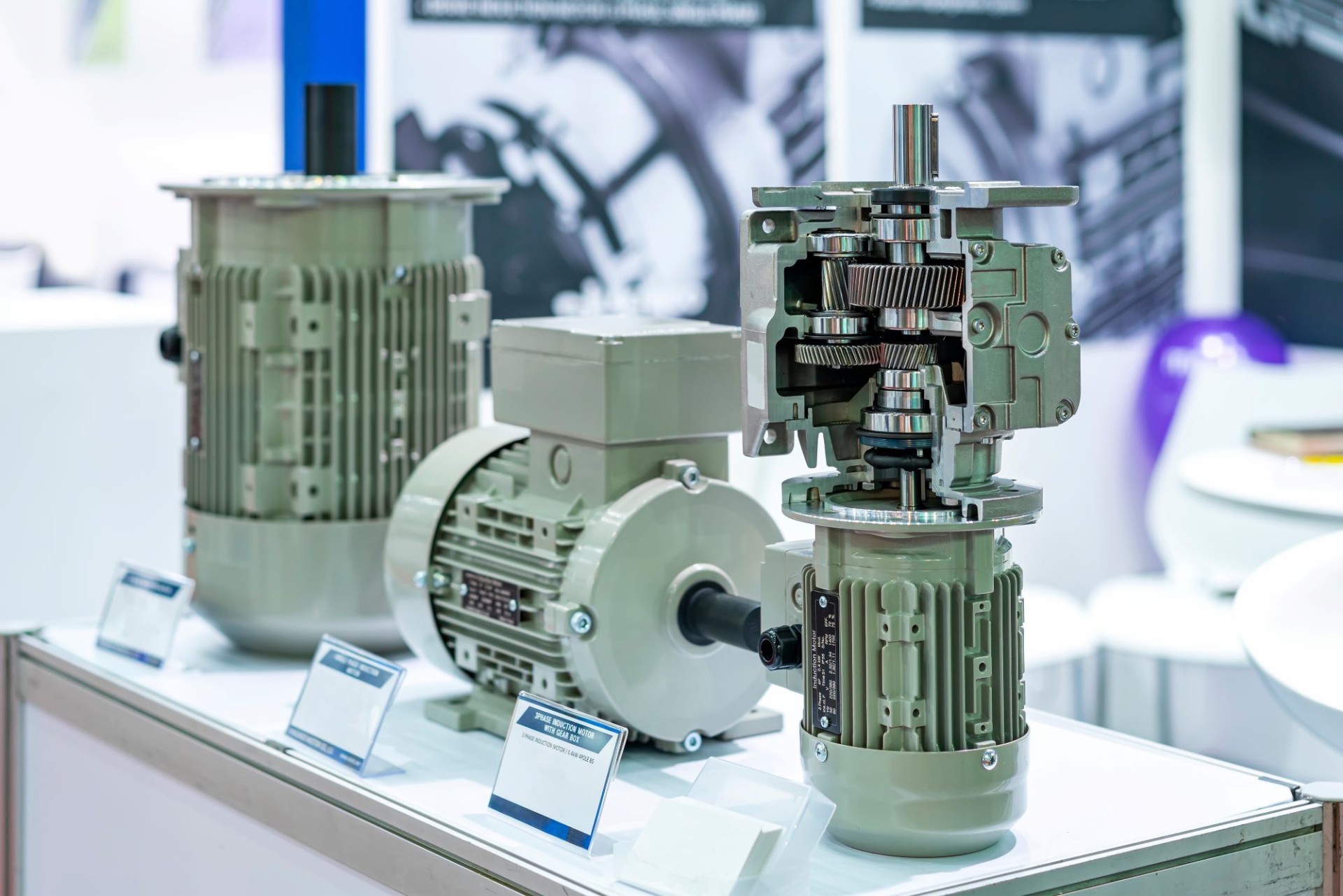
Overview of the Different Types of Speed Reducers
You may already know that speed reducers (gearboxes) are devices designed to convert the torque and speed of an upstream electric motor to meet the drive requirements of an application. But did you know there are several types of speed reducers?
Understanding the characteristics of different types of speed reducers allows for informed decisions that enhance safety, efficiency, durability, and system performance.
That’s why our team of electric motor system specialists has prepared this brief guide outlining the main types of mechanical speed reducers, detailing their advantages and key applications.
Gear Speed Reducers (Spur, Helical, Hypoid)
These are the most common speed reducers on the market. They use gears to transfer power between the input and output shafts.
This proven technology is ideal for industrial applications requiring high power and continuous-duty cycles.
Based on gear tooth configuration, there are several subtypes:
- Spur gears: The simplest type, with teeth parallel to the axis. They provide a cost-effective solution for straight-line transmissions with minimal complexity.
- Helical gears: Featuring angled teeth, these gears reduce noise and improve energy efficiency, especially for constant high-speed loads.
- Hypoid gears: Combining the compactness of bevel gears with improved tooth contact, they enable efficient power transmission in confined spaces.

Advantages:
- Robustness
- High efficiency
- Low maintenance
Applications:
- Conveyors
- Industrial pumps
- Machine tools
Worm Gear Speed Reducers
Consisting of a worm gear driving a toothed wheel, these mechanical reducers stand out for their ability to deliver high reduction ratios in a compact design. The sliding contact between components ensures quiet operation, though efficiency is slightly lower compared to gear reducers.

Advantages:
- Quiet operation
- Natural self-locking (particularly useful for lifting systems)
Applications:
- Elevators
- Inclined conveyors
- Handling equipment
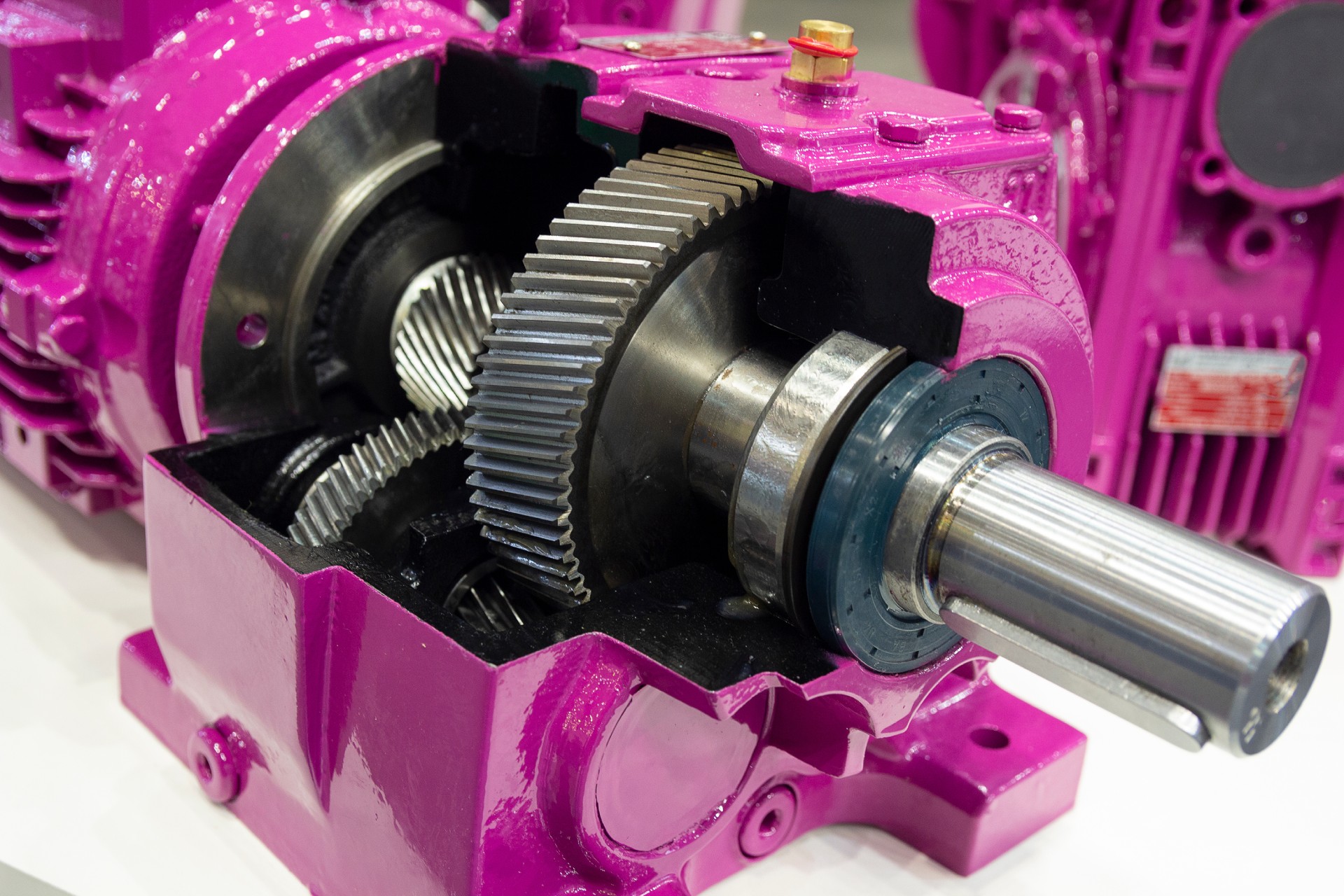
Planetary Speed Reducers
These systems are based on a central gear (the sun) surrounded by planetary gears held by an external ring. This design effectively distributes the load, providing high torque output in a compact format.

Advantages:
- High efficiency
- Compact design
- Excellent dynamic load tolerance
Applications:
- Industrial robots
- Medical imaging equipment
- Machine tools
Epicyclic Speed Reducers
Derived from planetary gearboxes, these reducers (also known as epicyclic planetary reducers) feature gears where the satellite pinions rotate around a central sun gear and are held by a carrier. This mechanism evenly distributes the load across the satellites, ensuring robust and efficient torque transmission in a compact space.

Advantages:
- High power-to-weight ratio
- Compact design
- High reliability
Applications:
- Industrial robots
- Wind turbines
- Heavy-duty conveyors
- Oil and gas equipment
Bevel Gear Speed Reducers
Bevel gear reducers transmit power through cone-shaped gears, allowing changes in shaft orientation. They are ideal for right-angle transmissions while offering precise speed and torque control.

Advantages:
- High precision
- Ability to transmit high loads
- Excellent reliability
Applications:
- Turbines
- Transportation systems
- Agricultural machinery
Discuss your needs with a gearbox specialist
Parallel Shaft Speed Reducers
These reducers align the input and output shafts for linear force transmission, maximizing efficiency. Their modular design allows easy customization to meet specific needs.

Advantages:
- High efficiency
- High load capacity
Applications:
- Assembly lines
- Industrial presses
Variable Speed Reducers
These systems use various mechanisms, such as adjustable pulleys or continuously variable gears, to adjust output speed without changing input speed. This provides maximum flexibility in machine performance control.

Advantages:
- Flexibility
- Precise speed control
Applications:
- Fans
- Centrifuges
- Dosing systems
Hollow Shaft Speed Reducers
With a hollow output shaft, these reducers can be mounted directly onto the driven equipment’s shaft. This design simplifies installation and minimizes the need for additional components.

Advantages:
- Quick installation
- Space-saving design
Applications:
- Packaging machines (wrapping, labeling, etc.)
- Conveyors
Gearmotors
Combining an electric motor with a speed reducer, these integrated devices provide an all-in-one solution for applications requiring compactness. Gearmotors can be customized based on torque, speed, and power requirements.

Advantages:
- Compact design
- Easy to install
- Ready to use
Applications:
- Industrial robots
- Handling equipment
Specialized Speed Reducers
In addition to traditional types, specialized models are designed for specific environments or requirements.
For example, stainless steel reducers are ideal for the food, pharmaceutical, or chemical industries, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are crucial. These reducers withstand frequent washing and chemical exposure, making them perfect for sterile environments.
Explosion-proof reducers (ATEX-certified) meet strict safety standards for oil, gas, and mining industries. Their design minimizes explosion risks in environments where flammable gases, vapors, or dust are present.

These specialized speed reducers demonstrate the adaptability of speed reduction technologies in the face of extreme environmental and industrial constraints.
Omnifab: Your Go-To Source for All Types of Speed Reducers
If you have further questions about different types of speed reducers (models, applications, top brands, etc.) or require the services of a technician for installation, maintenance, or repair, the Omnifab team is your best resource.
You’ll also be pleased to know that we supply reducers from recognized brands such as Nord Gear and SEW Eurodrive.
Contact us today, and we will promptly deploy the necessary resources to provide you with the best possible service.