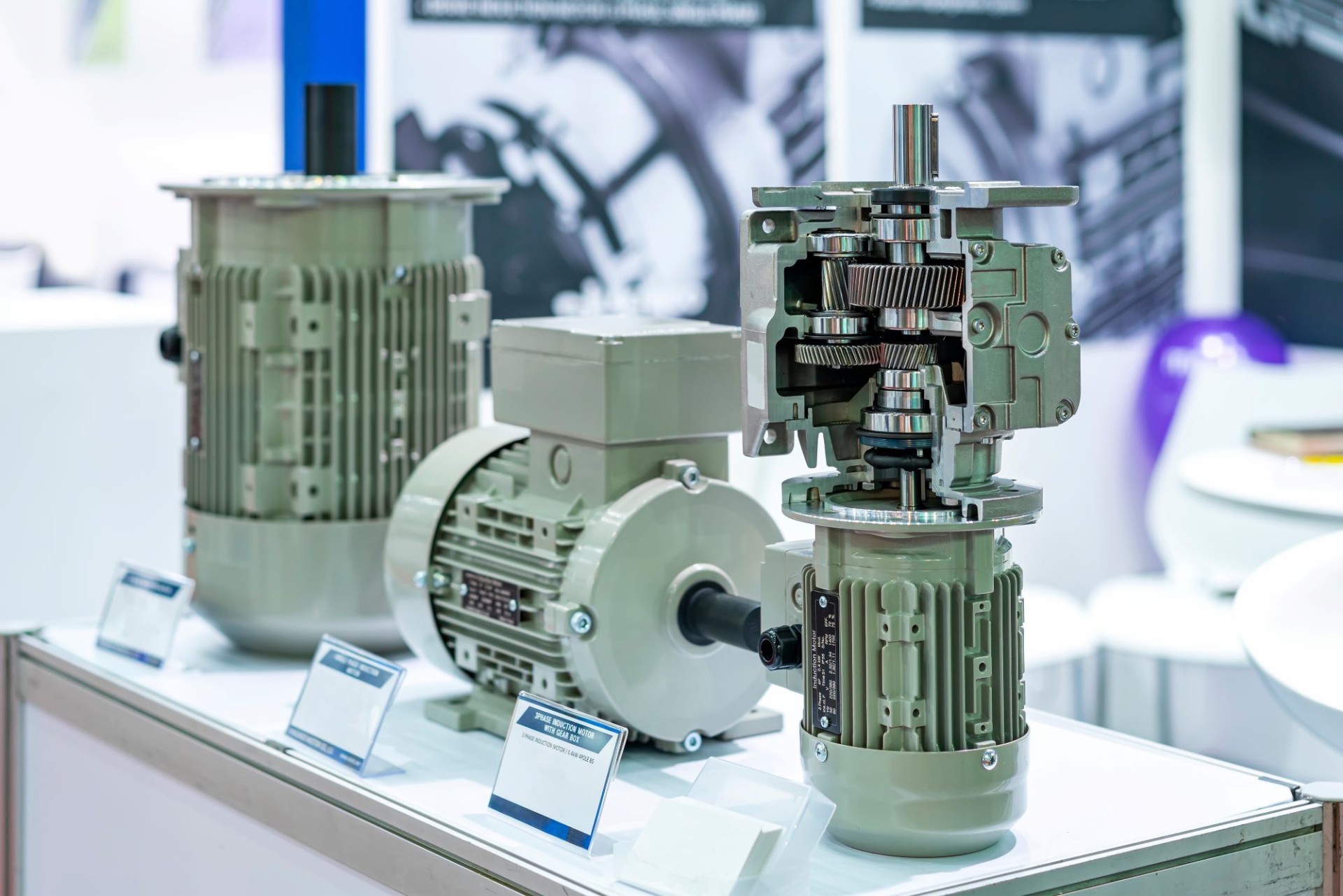
If you’re interested in gear motors, you’ve come to the right place to satisfy your curiosity! And if you’re wondering how to choose the right gear motor for a particular application, you’ll find the answers here as well.
Our experts know a lot about this subject related to electric motors, and they love sharing their knowledge.
So, get ready to learn a lot about the different types of gear motors, their uses, and their benefits as you read on!
What is a Gear Motor?
In general, a gear motor can be defined as the combination of an electric motor and a speed reducer within the same mechanical device.
They offer an efficient solution to match the speed and torque of an electric motor to the specific needs of a given application.
The Role of Gear Motors
The main function of a gear motor is to reduce the rotational speed of the electric motor while increasing the output torque.
In other words, it converts the high speed and low power of a motor into a slower speed but with greater rotational force. This allows for the use of less electrical power to move a given load.
Gear motors are widely used in various industrial and commercial applications, whether to move heavy loads at low speed or to provide high torque at reduced rotation speeds.
They are found in equipment such as:
- Conveyors
- Machine tools
- Lifting systems
- Automatic doors
- And more.
How a Gear Motor Works
In a gear motor, the electric motor provides the energy needed to drive the system. (Several types of electric motors can make up the “motor” part of a gear motor.)
Next, it’s in the “speed reducer” (or gearbox) where the rotational speed of the electric motor is reduced, and the output torque is increased. This part consists of several gears of different sizes that mesh with each other.
The reduction ratio, which is the ratio between the motor’s input speed and the gearbox’s output speed, determines how the speed and torque are modified. For example, a reduction ratio of 10:1 means that for each full rotation of the motor, the gearbox output rotates only one-tenth of a turn, but with ten times the rotational force.
During operation, when the electric motor is powered, it begins to rotate. This rotational movement is transmitted through the gears of the speed reducer, which reduces the rotational speed and increases the output torque.
Thus, the gear motor produces mechanical output suited to the specific needs of the application.
Types of Gear Motors
There are several types of gear motors, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Their name is based on the type of gear used to transmit motion.
Here are some of the most common types of gear motors:
Helical Gear Motors
They provide quiet operation, high efficiency, and good load capacity. They are commonly used in applications requiring precise movement and high torque transmission.
Bevel Gear Motors
These are often used when motion direction changes or right-angle transmissions are needed for an application. They typically offer good efficiency and high load capacity.
Worm Gear Motors
These gear motors use a worm screw to transmit power, allowing for a high reduction ratio in a compact size. They are known for their quiet operation and high precision.
Planetary Gear Motors
They provide a high reduction ratio in a compact size, along with great precision and high load capacity. They are commonly used in applications requiring high torque and low-speed operation.
Coaxial Gear Motors
They offer quiet operation, high efficiency, and high load capacity. They are recommended for generating precise motion and ensuring high torque transmission.
Discuss Your Gear Motor Needs with a Specialist
The Advantages of Gear Motors
There are several benefits to choosing a gear motor over a separate motor and speed reducer combination.
Here are the main ones:
Space Savings and Easy Integration
By combining the electric motor and speed reducer into a single unit, gear motors are often more compact and take up less space than systems requiring separate components. This facilitates integration into various applications and provides space savings.
Reliability, Durability, and Low Maintenance
Gear motors are typically designed to be robust and durable, making them reliable in demanding industrial environments. They also require less maintenance (lubrication, laser alignment, etc.), reducing long-term maintenance costs.
Energy Efficiency
By precisely adjusting the rotational speed of the electric motor to the speed required by the application, gear motors can contribute to more efficient energy use, which can lead to lower operating costs.
Noise Reduction
Gear motors typically generate less noise than motors coupled with separate speed reducers.
How to Choose a Gear Motor?
Here are some steps to guide you in the process of purchasing a gear motor:
1- Determine the Requirements of Your Application
First, take the time to identify your needs in terms of:
- Power
- Direction of movement
- Output torque and speed
- Reduction ratio
- Maximum input speed
- Suitable type of current
2 – Consider Space, Weight, and Noise Constraints
Ensure the chosen type of gear motor can be efficiently integrated into your system, taking space and weight constraints into account.
3 – Consider Environmental Conditions
If your application is subject to special environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, high humidity levels, or vibrations, choose a gear motor designed to withstand those conditions. You can rely on IP protection ratings for this.
4 – Consult a Specialist if Necessary
If you’re unsure about your choice or if your application is complex, it may be a good idea to consult a motorization specialist for additional advice.
Omnifab: A Gear Motor Reference in Quebec
If you have further questions related to gear motors (models, top brands, etc.) or need the services of a technician capable of repairing this equipment, Omnifab’s team is your best resource.
We are also proud to distribute and repair gear motors from well-known brands such as WEG and SEW Eurodrive.
Contact us now, and we will quickly mobilize the necessary resources to assist you.